Many B2B companies grapple with a common challenge: data collection.
They often find themselves at a crossroads, uncertain about what data to collect.
In contrast to B2C businesses, which can easily amass customer data for analysis, B2B enterprises seemingly have access to fewer data sources.
Today, we aim to shed light on the data that B2B businesses should prioritize collecting.
Define Your Data Collection Goals
First and foremost, it’s crucial to ask the fundamental question: What are your objectives for collecting data? In other words, what insights do you hope to glean from this data?

Are you seeking to gain insights into your sales performance or understand user behavior?
For example, suppose you have just launched a new feature in your application and you want to know whether users will find this feature useful and under what circumstances they will use it, then you need to consider the collection of user behavior data.
Another case will be you want to know what your user finds your product or service. How do they feel when they are using your service? Do they trust your brand or business? Are they happy with the stages they go through when interacting with your business?
Then, you need to collect data for opinions and feedback. It’s worth noting that these data may carry some bias, as they involve subjective judgments or responses that may be socially acceptable rather than authentic.
However, relying solely on observed behavior doesn’t always uncover the reasons behind users’ actions or their emotions. Therefore, it’s beneficial to employ various data collection methods to gain diverse perspectives and answer a wide range of questions.

Defining your goals is the first step in implementing data strategies, whether in data collection or analysis.
If you’re uncertain about the questions your data can answer or the insights it can provide, we’ve outlined 5 key objectives and the relevant metrics to collect for your business.
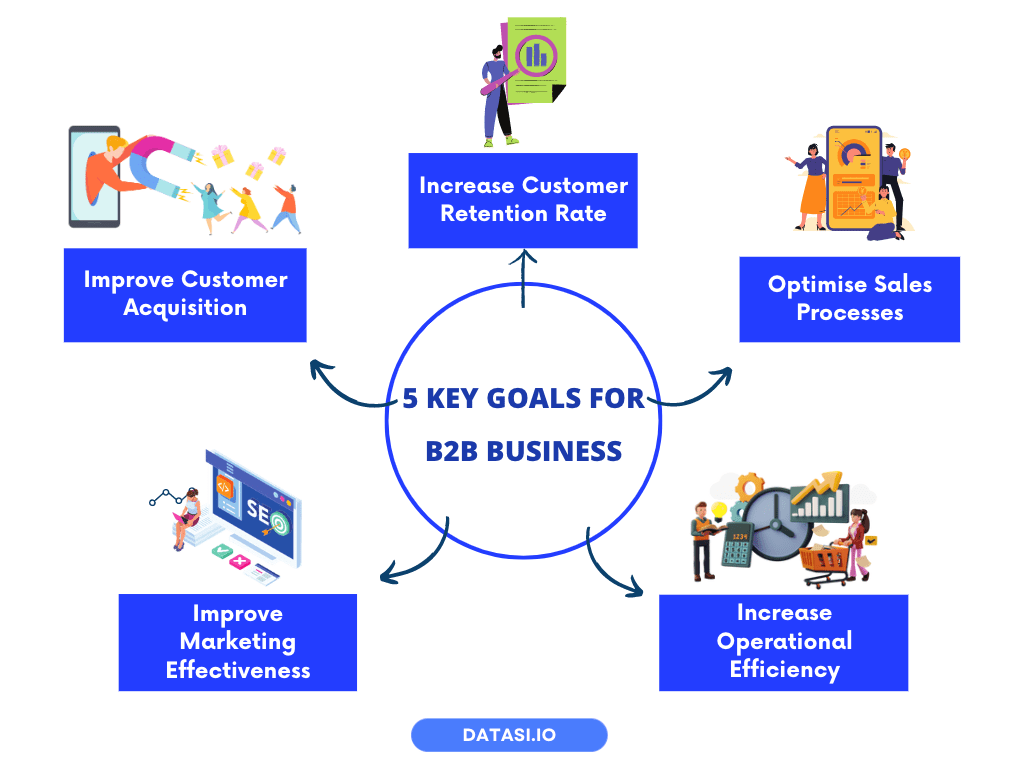
Goal: Improve Customer Acquisition
For B2B businesses, understanding your customers or prospects is paramount.
You can start by collecting prospects’ demographic data including gender, email, location, and job titles.
This knowledge enables you to identify key contacts within a company and tailor your communication accordingly.
At the same time, you can match your salespeople to prospects based on location and language facilitating more effective interactions.

As you gather more information about your prospects or their companies, expand your data to include acquisition channels. Identify which channels or touchpoints prospects convert through—email, referrals, or websites through web analytics tools.
Over time, you can build a prospect database that allows you to calculate conversion rates for each channel, pinpointing the most effective ones.
Goal: Increase Customer Retention
It’s a well-known fact that 80% of a company’s earnings come from 20% of its loyal customers.
Cultivating customer loyalty among existing clients is more cost-effective than acquiring new ones. Thus, it’s essential to manage your relationships with customers and enhance customer retention rates.
This entails listening to customer feedback, addressing their needs, and surpassing their expectations.
For instance, you can collect data on customer satisfaction scores and feedback as indicators of their experience with your product or service. Then, utilize this information to make necessary optimizations.
However, remember that not all customers hold the same value. You should not spend the same amount of effort and attention on all customers.
You can use 2 ways to analyze and estimate the value of a customer such as RFM analysis or calculating Customer Lifetime Value (CLV).
RFM analysis (Recency, Frequency, Monetary value) segments customers based on loyalty, activity, and spending power.
By categorizing customers into different tiers, you can tailor strategies to each group’s needs.
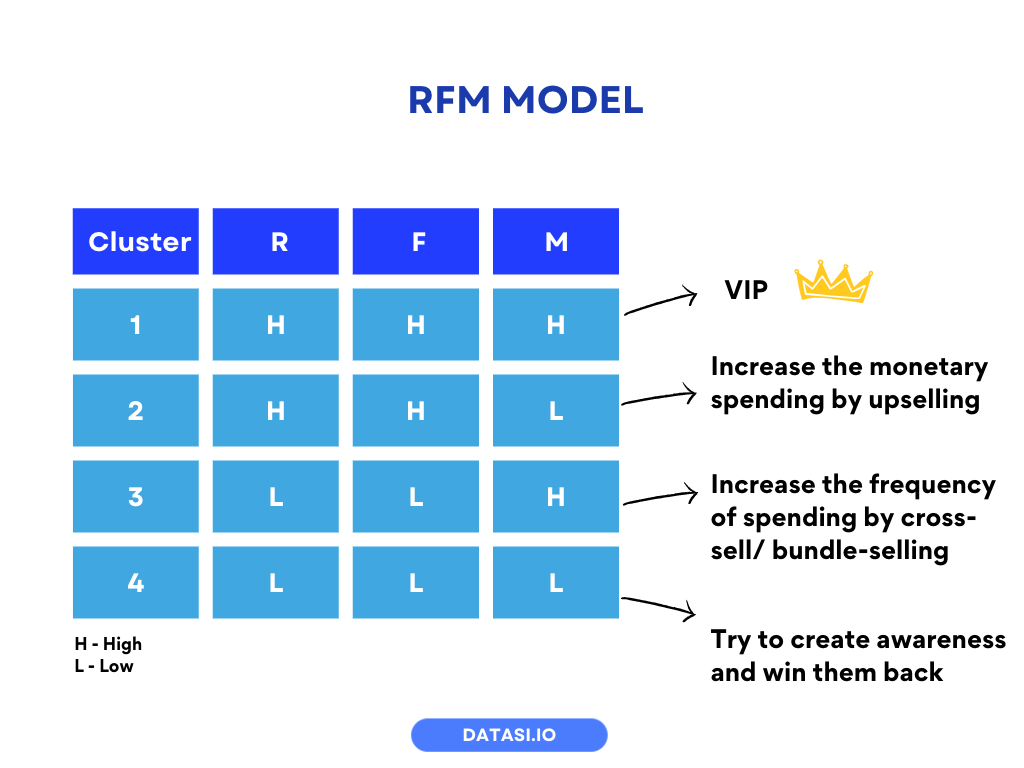
For instance, customers in cluster 1 with high scores for all 3 dimensions are your most valuable clients. You should divert more energy and resources into this group of customers. Provide them with customized offers and personalized services to manage the relationships.
While the customers in cluster 4, are the least valuable members. What you can do is create more awareness for this group of customers to get them interested in your offering.
Another important concept in customer relationship management is understanding the lifetime value of a customer.
Customer lifetime value (CLV) is the total amount of money a customer is expected to spend with your product or service during the lifetime of an average business relationship.
By understanding your customer’s CLV, you are able to identify who is your most profitable customers and provide personalized solutions accordingly.
[mailerlite_form form_id=2]

Goal: Optimize Sales Processes
Tracking the sales cycle and prospects’ stage within it is crucial for businesses. It provides insights into conversion rates at each stage and informs optimization efforts.
Different businesses have distinct sales cycles, but common stages include prospecting, contact, demonstration or proposal, follow-up, and closing.
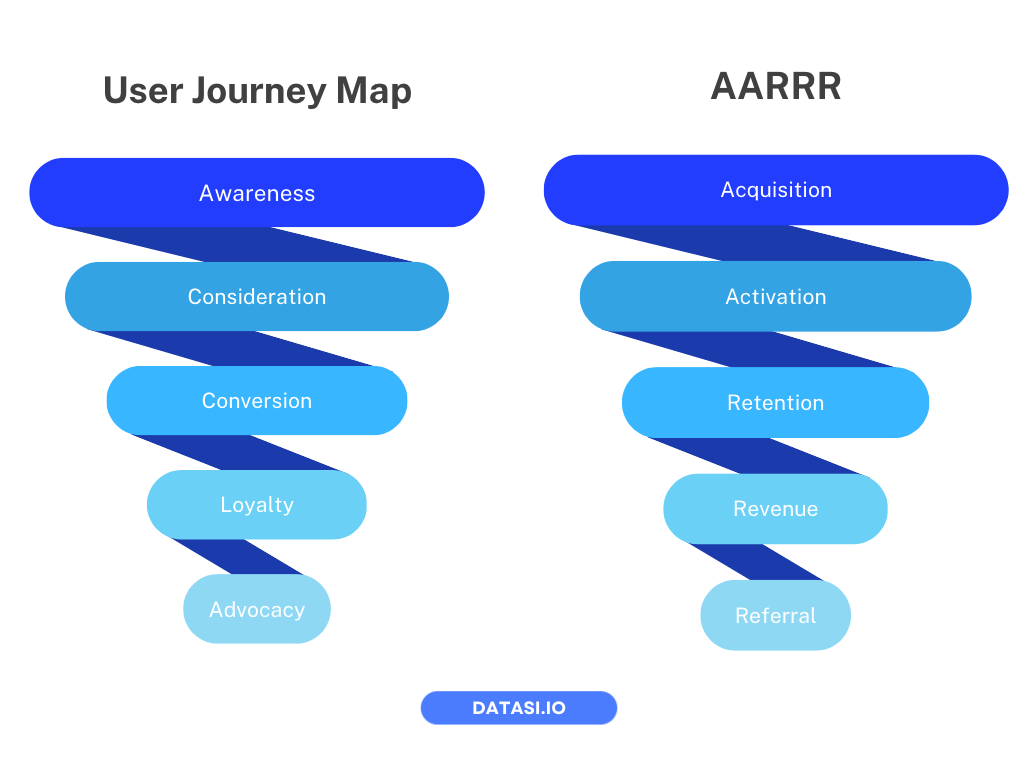
Collect data at each stage of your sales cycle or use established frameworks like the AARRR Pirate Metrics or User Journey Map (UJM) to break down the customer lifecycle. Monitoring and tracking customer interactions at each stage facilitate better understanding and more effective optimization.
Goal: Improve Marketing Effectiveness
Tracking online marketing metrics is vital for assessing lead sources and evaluating online marketing efforts.
Employ web analytics tools like Google Analytics to gain insights into lead generation channels, customer engagement, and the effectiveness of marketing messages.
However, when conducting analytics for marketing efforts, be aware of these 6 common mistakes.
Goal: Increase Operational Efficiency
Internally, data plays a critical role in monitoring performance, tracking goals, and assessing progress.
Companies use various indicators to measure employee productivity, process efficiency, and supply chain metrics. These metrics ensure high workforce productivity, alignment with business goals, and transparency within the team.
Next Steps After Data Collection
Once you’ve identified the data you wish to collect and have gathered the necessary information, consider using a Business Intelligence (BI) tool to consolidate your data into a centralized dashboard for efficient monitoring.

Before collecting data, emphasize the importance of data quality. Poor-quality data yields inaccurate or low-quality outputs. Implement standards and frameworks for data collection to ensure data quality, accuracy, and usability.
If you want to know more in detail about different ways of data collection, you can continue reading here or consult with our resourceful experts.

Talk to us today
Find out how we can help your business to build a successful data strategy.


